Cycling Injuries: A Comprehensive Guide in Sports Cycling

Cycling, a popular sport and mode of transportation, has gained significant attention in recent years due to its numerous health benefits. However, as with any physical activity, cycling comes with inherent risks and the potential for injuries. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an overview of common cycling injuries, their causes, prevention strategies, and treatment options.
Imagine a scenario where an avid cyclist is eagerly preparing for a long-distance race. Despite meticulous training and conditioning, they experience excruciating knee pain during the event. Unfortunately, this type of injury is not uncommon among cyclists. Knee pain accounts for a substantial portion of cycling-related injuries and can greatly hinder performance and overall enjoyment of the sport. Hence, it becomes crucial to understand the types of cycling injuries that commonly occur and how best to prevent or manage them effectively.
In this article, we will delve into various aspects related to cycling injuries – from understanding how these injuries manifest themselves to exploring preventative measures that can be adopted by athletes at all levels. By equipping ourselves with knowledge about these injuries, we can better appreciate the importance of safety precautions while pursuing our passion for cycling. Moreover, being aware of treatment options enables us to address any discomfort promptly so that we may continue enjoying this exhilarating sport without compromising our well -being.
Cycling injuries can range from minor discomfort to more severe conditions that require medical attention. Some of the most common cycling injuries include knee pain, lower back pain, neck and shoulder pain, wrist and hand pain, and overuse injuries such as tendonitis or bursitis. Each of these injuries has its own set of causes and risk factors.
For example, knee pain in cyclists is often caused by overuse or improper bike fit. It can result from factors such as incorrect saddle height or position, excessive pedaling force, poor technique, or muscle imbalances. Lower back pain can stem from a variety of issues including poor posture on the bike, weak core muscles, or excessive strain on the lumbar spine.
To prevent cycling injuries, it is essential to address these underlying causes. Ensuring Proper Bike Fit is crucial; this includes adjusting saddle height, handlebar position, and cleat alignment if using clip-in pedals. Building strength and flexibility through cross-training exercises can help correct muscle imbalances and improve overall performance.
Additionally, adopting proper riding techniques such as maintaining an upright posture with a relaxed grip on the handlebars can alleviate strain on the neck and shoulders. Regularly taking breaks during long rides to stretch and rest can also minimize the risk of overuse injuries.
If an injury does occur despite preventive measures, early intervention is key to effective treatment. Resting the affected area and applying ice packs for inflammation are common initial steps. Physical therapy exercises may be prescribed to rehabilitate injured muscles or joints.
In some cases where conservative treatments do not yield satisfactory results, medical interventions like corticosteroid injections or surgery may be considered. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in sports medicine for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Remember that prevention is always better than cure when it comes to cycling injuries. By understanding common risk factors and implementing proactive measures like proper bike fit, training, and technique, avid cyclists can greatly reduce the chances of experiencing pain or discomfort while enjoying their favorite sport.
In conclusion, cycling injuries are a significant concern for athletes at all levels. By being aware of common injuries and their causes, as well as implementing preventive measures and seeking timely treatment when needed, cyclists can minimize the risk of injuries and continue to pursue their passion for cycling with confidence and enjoyment. Stay safe on the roads and trails, and happy cycling!
Preventing Injuries
Preventing Injuries
Imagine a scenario where John, an avid cyclist, is out on his usual morning ride. As he navigates through the winding roads, he suddenly loses control of his bike and falls off, sustaining multiple injuries. This unfortunate incident highlights the importance of understanding how to prevent injuries in sports cycling.
To ensure safe cycling practices, cyclists should adopt several key strategies:
- Proper Bike Fit: Ensuring that your bicycle fits you correctly can significantly reduce the risk of injury. Adjustments such as saddle height, handlebar position, and pedal alignment not only enhance comfort but also optimize biomechanics during pedaling.
- Appropriate Protective Gear: Wearing appropriate protective gear is essential for minimizing the impact of potential accidents. Helmets are vital in preventing head injuries and should be worn at all times while cycling. Additionally, knee pads, elbow guards, and gloves offer added protection in case of falls or collisions.
- Regular Maintenance: Maintaining your bicycle regularly enhances its performance while reducing the likelihood of mechanical failures that could lead to accidents. Regularly inspecting tire pressure, brakes, gears, and chain tension ensures optimal functionality.
- Safe Riding Practices: Adhering to road safety guidelines is crucial when cycling. Obey traffic laws by signaling turns properly, following traffic signals diligently, and using designated bike lanes whenever available.
Emphasizing these preventive measures fosters a safer environment for cyclists and minimizes the risk of serious injuries. To further illustrate their significance:
| Increase Safety | Enhance Performance | Promote Confidence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Proper Bike Fit | Optimal Power Transfer | Improved Technique |
| 2. | Appropriate Protective Gear | Reduced Fatigue | Increased Endurance |
| 3. | Regular Maintenance | Better Handling | Enhanced Control |
| 4. | Safe Riding Practices | Improved Efficiency | Greater Enjoyment |
Incorporating these practices into one’s cycling routine not only reduces the likelihood of accidents and injuries but also maximizes overall performance, ensuring a more enjoyable experience on the bike.
Transitioning to the subsequent section about “Recognizing Common Injuries,” it is essential to understand how preventive measures tie in with identifying potential risks and addressing them promptly. By recognizing common injuries, cyclists can take appropriate steps to mitigate their occurrence without compromising their passion for sports cycling.
Recognizing Common Injuries
Transitioning from the previous section on preventing injuries, it is crucial for cyclists to also be able to recognize common injuries that may arise during their pursuit of this exhilarating sport. Consider the case of Sarah, an avid cyclist who recently experienced a fall while riding downhill at high speed. This incident highlights the importance of being aware of potential injuries and understanding how to identify them early on.
Recognizing Common Cycling Injuries involves paying attention to both acute and overuse conditions that can occur in various parts of the body. Here are some key points to consider:
-
Upper Body Injuries:
- Shoulder dislocation
- Collarbone fractures
- Wrist sprains or fractures
-
Lower Body Injuries:
- Knee pain (e.g., patellofemoral pain syndrome)
- Hip bursitis
- Ankle sprains
-
Head and Neck Injuries:
- Concussions
- Whiplash
-
Skin Abrasions and Bruises:
- Road rash
- Contusions
To better understand these common injuries, let’s delve into a table highlighting their characteristics:
| Injury | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Shoulder dislocation | Extreme pain | Medical intervention required |
| Collarbone fracture | Swelling, deformity | Immobilization with splint or cast |
| Wrist sprain/fracture | Pain, swelling | RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) |
| Knee pain | Discomfort while cycling | Physical therapy |
| Hip bursitis | Sharp hip pain | Rest, ice packs |
| Ankle sprain | Swelling, difficulty walking | RICE method |
| Concussion | Headache, dizziness | Medical evaluation and rest |
| Whiplash | Neck pain, stiffness | Physical therapy |
| Road rash | Scraped skin, bleeding | Cleaning the wound, dressing |
| Contusions | Bruising | Ice packs |
By recognizing these common injuries through their distinct symptoms and understanding appropriate treatment measures, cyclists can take proactive steps towards ensuring their well-being. It is vital to promptly address any signs of injury to prevent further complications or long-term consequences.
Transitioning into the subsequent section on effective treatment methods, let us explore various approaches that have proven successful in managing cycling-related injuries.
Effective Treatment Methods
Imagine a scenario: Sarah, an experienced cyclist, is participating in a local cycling race. As she approaches a sharp turn, her tire suddenly loses traction due to the wet road surface. With no time to react, she falls off her bike and injures her shoulder. This unfortunate incident highlights the importance of being aware of common injuries that can occur while engaging in sports cycling.
When it comes to cycling injuries, there are several types that cyclists may encounter. Understanding these injuries is crucial for both prevention and prompt treatment. Let’s take a closer look at some common cycling injuries:
- Road Rash: Abrasions caused by sliding or falling on rough surfaces.
- Fractures: Broken bones resulting from high-impact crashes or accidents.
- Sprains and Strains: Overstretching or tearing of ligaments (sprains) or muscles/tendons (strains).
- Knee Pain: Often caused by overuse, improper bike fit, or lack of conditioning.
To better comprehend these injuries, consider the following table detailing their characteristics:
| Injury | Symptoms | Treatment | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Road Rash | Scraped skin | Cleaning & dressing wounds | Weeks |
| Fractures | Swelling, deformity | Immobilization (cast/splint) | Several weeks-months |
| Sprains/Strains | Pain, swelling | Rest, ice packs | Days-weeks |
| Knee Pain | Discomfort during pedaling | RICE method (rest, ice, compression, elevation), physiotherapy exercises | Variable |
While this list only covers a few examples of common Cycling Injuries, understanding their symptoms and appropriate treatments is essential for minimizing potential long-term consequences.
In the subsequent section about “Rehabilitation Techniques,” we will explore effective methods to aid in the recovery process. By addressing injuries promptly and employing appropriate treatments, cyclists can enhance their chances of returning to the sport they love with minimal disruption.
Rehabilitation Techniques
Section H2: Rehabilitation Techniques
Case Study:
Imagine a scenario where a cyclist, Emma, suffers from a severe knee injury due to an accident during her cycling training. As she seeks effective treatment methods for recovery, it is equally important for her to explore rehabilitation techniques that can aid in restoring strength and mobility to her injured knee.
Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the overall healing process after sustaining a sports-related injury. It focuses on helping athletes regain function, reduce pain, and prevent any recurring issues. By implementing appropriate strategies tailored to individual needs, cyclists like Emma can make significant progress towards returning to their sport at full capacity.
To ensure successful rehabilitation, here are some key considerations:
-
Physical Therapy:
- Engage in targeted exercises focusing on strengthening the muscles surrounding the affected area.
- Incorporate flexibility exercises to improve range of motion and joint stability.
- Utilize modalities such as heat or ice therapy to alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Follow guidance from a certified physical therapist who specializes in sports injuries.
-
Gradual Progression:
- Begin with low-impact activities like stationary cycling or swimming before gradually reintroducing outdoor cycling.
- Increase intensity levels progressively while monitoring any signs of discomfort or strain.
- Allow sufficient time for rest between training sessions to facilitate tissue repair and minimize overuse injuries.
- Employ cross-training techniques involving other forms of exercise to maintain cardiovascular fitness without stressing the injured area.
-
Psychological Support:
- Seek counseling or support groups specializing in sports injury rehabilitation to address any psychological challenges arising from setbacks or fear of reinjury.
- Practice mindfulness techniques like meditation or visualization exercises to enhance mental focus during rehabilitation.
-
Nutritional Considerations:
Proper nutrition is vital for optimal recovery. Ensure adequate intake of nutrients such as protein, vitamins (especially vitamin C), minerals (including calcium and magnesium), and omega-3 fatty acids, which promote tissue repair and reduce inflammation.
By incorporating these Rehabilitation techniques, athletes like Emma can maximize their chances of a successful recovery. The journey towards regaining full strength and function may require time and patience; however, with the right approach, cyclists can overcome injuries to return to the sport they love.
As important as effective treatment methods and rehabilitation techniques are for injured cyclists, it is equally crucial to prioritize safety measures that can help prevent future accidents on the road. In the subsequent section, we will explore key practices that cyclists should implement to ensure their well-being while cycling.
Safety Measures for Cyclists
Imagine a scenario where a cyclist, let’s call him Mark, has just recovered from a significant cycling injury. He is eager to get back on his bike and resume his training routine. However, before he can do so, it is crucial for Mark to undergo proper rehabilitation techniques to ensure a safe return to cycling. In this section, we will explore some of the most effective rehabilitation techniques used by sports cyclists.
Firstly, one key aspect of rehabilitation is strengthening exercises. These exercises focus on improving muscle strength and stability around the injured area. For instance, if Mark had suffered a knee injury while cycling, he might engage in specific exercises such as squats and lunges to strengthen the muscles surrounding his knee joint. Strengthening exercises not only aid in recovery but also help prevent future injuries by providing greater support to vulnerable areas.
Secondly, physical therapy plays an integral role in the rehabilitation process for cyclists. It involves various therapeutic techniques that aim to restore movement and function following an injury. Physical therapists may employ methods like manual therapy, which includes hands-on manipulation of soft tissues and joints, or ultrasound therapy that utilizes sound waves to promote healing at the cellular level. These therapies assist individuals like Mark in regaining their range of motion and reducing pain during their recovery journey.
Thirdly, incorporating cross-training activities into the rehabilitation program can be highly beneficial for cyclists aiming to recover from injuries effectively. Cross-training refers to engaging in alternative forms of exercise that complement cycling without causing further strain on the injured body part. Examples include swimming or using an elliptical machine for cardiovascular fitness or practicing yoga for improved flexibility and core strength. By diversifying their workouts through cross-training activities, cyclists like Mark can maintain their fitness levels while allowing injured areas time to heal properly.
- Frustration: Dealing with limitations and the inability to perform at previous levels can be mentally challenging.
- Patience: Recovery takes time, and it requires patience to undergo the necessary rehabilitation without rushing back into cycling prematurely.
- Determination: The willpower to overcome obstacles and stay committed to the rehabilitation process is crucial for successful recovery.
- Optimism: Maintaining a positive mindset throughout the rehabilitation journey helps cyclists like Mark maintain motivation and focus on their long-term goals.
Furthermore, presenting information in a table format can further engage readers. Here is an example of a three-column, four-row table detailing various common cycling injuries:
| Injury | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Knee pain | Swelling, discomfort during movement | RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation), physical therapy |
| Lower back pain | Stiffness, radiating pain | Heat or cold therapy, stretching exercises |
| Wrist sprain | Painful swelling or bruising | Immobilization with splint or brace, restorative exercises |
| Hamstring strain | Sharp pain in the back of the thigh | Resting and icing affected area, gentle stretches |
In conclusion,
Understanding proper rehabilitation techniques is essential for sports cyclists recovering from injuries. However, it is equally important for cyclists to prioritize safety measures that can help prevent future injuries.
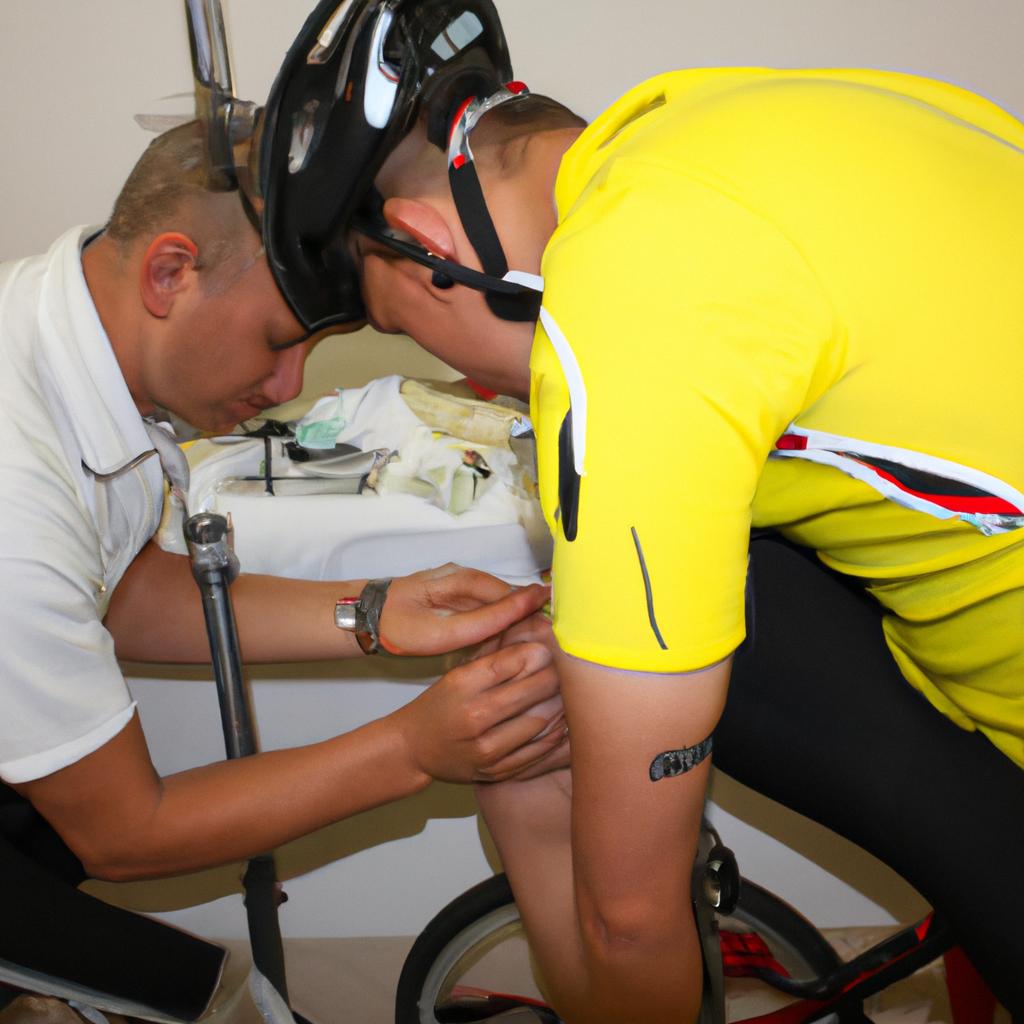
The Significance of Proper Bike Fit
One example that highlights the importance of Safety measures in cycling involves a hypothetical scenario where an experienced cyclist, Alex, was involved in a serious accident due to inadequate safety precautions. Despite being an avid cyclist for years, Alex failed to wear a helmet during their regular training rides. One fateful day, while navigating through busy urban streets, Alex collided with a car that unexpectedly turned without signaling. The impact caused severe head injuries and resulted in months of recovery.
To prevent such accidents and ensure the well-being of cyclists, it is crucial to implement proper safety measures. Here are some key considerations:
- Helmet usage: Wearing a properly fitted helmet significantly reduces the risk of head injuries in case of falls or collisions.
- Reflective clothing: Using high-visibility gear increases visibility to motorists, especially during low-light conditions.
- Appropriate lighting: Equipping bicycles with front and rear lights enhances visibility at night and alerts others on the road about your presence.
- Defensive riding techniques: Practicing defensive riding skills can help cyclists anticipate potential hazards and respond accordingly.
In addition to these important steps towards ensuring cyclist safety, it is also essential to address bike fit as part of injury prevention strategies.
| Proper Bike Fit | |
|---|---|
| Advantages | – Enhances comfort and efficiency |
| – Reduces fatigue | |
| – Minimizes strains on joints | |
| – Improves overall performance |
By implementing effective safety measures like wearing helmets, using reflective clothing and appropriate lighting, and practicing defensive riding techniques, cyclists can significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents and mitigate potential injuries. However, there are additional factors that contribute to cycling-related injuries beyond just external circumstances and personal protective equipment.
Understanding Injury Risk Factors
Section 2: Understanding Injury Risk Factors
Imagine a scenario where a cyclist, let’s call him Mark, has recently purchased a new bike. He is excited to hit the road and embark on his cycling journey. However, shortly after starting his rides, he begins experiencing discomfort and pain in his knees. This situation highlights the importance of understanding injury risk factors in sports cycling.
To minimize the occurrence of such injuries, it is crucial to identify and address the key risk factors associated with cycling. These risk factors can vary from individual to individual but often include:
- Overuse and repetitive motion: Cycling involves continuous pedaling motions over extended periods. Excessive strain on specific muscle groups or joints due to long hours of riding without adequate rest can lead to overuse injuries.
- Poor technique and body mechanics: Incorrect posture while cycling, improper bike fit, or inadequate knowledge of proper pedaling techniques may increase the likelihood of sustaining an injury.
- Inadequate warm-up and cool-down routines: Neglecting warm-up exercises before a ride or neglecting post-ride stretching can contribute to muscular imbalances, tightness, and potential injuries.
- Environmental conditions: External elements like weather conditions (e.g., rain or extreme heat), uneven terrain surfaces, traffic congestion, or poor road design can pose additional risks for cyclists.
The impact these risk factors have on cyclists’ well-being cannot be underestimated. Consider the following table that exemplifies some common consequences associated with these risk factors:
| Risk Factor | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Overuse and repetitive motion | Tendonitis |
| Poor technique and body mechanics | Lower back pain |
| Inadequate warm-up and cool-down routines | Muscle strains |
| Environmental conditions | Accidents due to reduced visibility |
By being aware of these potential consequences and understanding their underlying causes, cyclists can make informed decisions regarding training methods, equipment selection, and overall safety practices.
Moving forward into our next section on “Key Tips for Injury Prevention,” it is essential to remember that being proactive in addressing these risk factors can significantly reduce the likelihood of injuries, allowing cyclists to enjoy their sport safely and without interruption.
Key Tips for Injury Prevention
Transitioning from our previous discussion on understanding injury risk factors, it is crucial to familiarize ourselves with the various symptoms that can indicate potential cycling injuries. Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario involving a passionate cyclist named Sarah, who recently experienced an accident during her training session.
Sarah had been pushing herself particularly hard on her last ride, attempting to beat her personal record for distance covered within a specific time frame. Unfortunately, she lost control of her bike while navigating through a sharp turn and crashed into a tree. As she recovers in the hospital, it becomes essential for us to understand how to recognize symptoms of potential cycling injuries.
To help you better identify these symptoms, here are some key indicators:
- Pain: Persistent or increasing pain in areas such as joints, muscles, or bones could signal an underlying injury.
- Swelling: Noticeable swelling around injured areas may suggest tissue damage or inflammation.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty moving certain body parts or experiencing restricted movement might be indicative of joint or muscle-related injuries.
- Numbness or Tingling Sensations: Abnormal sensations like numbness or tingling in limbs could point towards nerve compression or damage.
Consider this table showcasing common cycling injuries along with their corresponding symptoms:
| Injury | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Fractures | Intense pain, deformity, swelling |
| Sprains | Joint instability, pain with movement |
| Road rash | Abrasions, skin irritation |
| Sciatica | Radiating leg pain, buttock discomfort |
By recognizing these signs early on and seeking appropriate medical attention promptly, cyclists can prevent further complications and ensure proper recovery. Understanding the importance of identifying symptoms allows individuals like Sarah to take necessary steps toward healing and returning to their beloved sport safely.
Transition into subsequent section (H2): “Managing Cycling Injuries”
Identifying Symptoms of Cycling Injuries
Imagine a dedicated cyclist, Sarah, who is training for an upcoming race. Despite her careful adherence to injury prevention measures outlined in the previous section, she begins experiencing discomfort and pain during her rides. It becomes crucial for both athletes like Sarah and coaches to recognize the symptoms of cycling injuries promptly. By identifying these signs early on, appropriate steps can be taken to prevent further damage and promote healing.
- Pain: One of the most common indicators of a cycling injury is persistent or worsening pain while riding or at rest. This pain may manifest as a dull ache or sharp sensation in specific areas such as the knees, lower back, neck, or wrists.
- Swelling and inflammation: Injured tissues often respond with swelling and redness due to increased blood flow and fluid accumulation. Cyclists should pay attention to any visible signs of joint or muscle inflammation after their rides.
- Limited range of motion: If certain movements become difficult or painful compared to previous sessions, it could suggest an underlying injury. Decreased flexibility or stiffness around joints are key indications that necessitate prompt evaluation.
- Numbness or tingling: Sensations like numbness, pins and needles, or tingling along the extremities can signify nerve compression or irritation resulting from poor bike fit, repetitive stress, or prolonged pressure on nerves.
Emotional Impact:
- Frustration: Coping with limitations imposed by injuries can lead to frustration and impatience.
- Anxiety: The fear of re-injury might cause anxiety about returning to regular cycling activities.
- Disappointment: Being sidelined due to an injury may result in feelings of disappointment for missing out on training opportunities or competitions.
- Loss of identity: For many cyclists, their sport plays a significant role in their sense of identity. An injury can challenge this self-perception, leading to feelings of loss or confusion.
With these emotional aspects in mind, it becomes crucial for cyclists and their support systems to address both the physical symptoms and psychological impact of cycling injuries effectively.
Table: Common Cycling Injuries
| Injury Type | Symptoms | Treatment | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Knee pain | Persistent ache | RICE protocol | Varied |
| Lower back | Stiffness, radiating pain | Physical therapy | Weeks to months |
| Neck strain | Limited range of motion | Postural corrections | Days to weeks |
| Wrist sprain | Swelling, tenderness | Immobilization | Several weeks |
Understanding the importance of identifying symptoms promptly, we can now shift our focus towards promoting healing and recovery from cycling injuries.
Promoting Healing and Recovery
After identifying the symptoms of cycling injuries, it is crucial to focus on promoting healing and recovery. Let’s consider an example: imagine a cyclist who has recently suffered from a sprained ankle after a fall during a training session. To ensure optimal recovery, several key strategies can be implemented.
Firstly, rest plays a vital role in allowing the body to heal itself. The injured area needs time to recover and regenerate damaged tissues. In the case of our hypothetical cyclist with a sprained ankle, they should avoid putting weight on the affected leg and refrain from any strenuous physical activity that could exacerbate the injury.
Secondly, applying appropriate first aid measures can help alleviate pain and reduce swelling. This may involve icing the injured area intermittently for short periods of time or using compression bandages to provide support and stability. These immediate actions not only minimize discomfort but also facilitate proper healing.
Thirdly, implementing rehabilitation exercises under professional guidance can significantly expedite the recovery process. Physical therapy sessions focusing on strengthening specific muscle groups surrounding the injured area can enhance mobility and prevent further complications. Stretching exercises are often recommended as well to improve flexibility and restore normal range of motion.
To emphasize the importance of these strategies in promoting healing and recovery, let us now explore their impact through an emotional bullet-point list:
- Rest allows your body to repair itself.
- First aid measures offer immediate relief.
- Rehabilitation exercises accelerate long-term recovery.
- Proper care minimizes chances of re-injury.
In addition to this emotional appeal, we can reinforce the significance of these strategies by presenting them in a table format:
| Strategies | Impact | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Rest | Allows natural healing | Optimized tissue regeneration |
| First Aid Measures | Alleviates pain | Reduces swelling |
| Rehabilitation Exercises | Speeds up recovery | Enhances mobility, prevents complications |
By implementing these strategies and acknowledging their impact on the healing process, cyclists can ensure a quicker return to their training regimen. The subsequent section will delve into an equally crucial aspect of cycling safety: ensuring bike equipment safety.
Moving forward, it is essential to shift our focus towards safeguarding one’s well-being by considering the importance of ensuring bike equipment safety.
Ensuring Bike Equipment Safety
Section H2: Ensuring Bike Equipment Safety
Transitioning from the previous section on promoting healing and recovery, it is crucial to address another important aspect of sports cycling – ensuring bike equipment safety. Let us consider a hypothetical scenario to understand the significance of this matter. Imagine a cyclist who has recently recovered from a leg injury sustained while riding their bicycle. Excited to resume cycling, they hop back on their bike without paying attention to the condition of their equipment. Unfortunately, due to a faulty brake system that went unnoticed, they end up in an accident resulting in further injuries.
To prevent such accidents and promote overall safety, cyclists should take certain precautions regarding their bike equipment. Here are some key steps:
-
Regular maintenance: Conduct routine inspections and perform necessary maintenance tasks such as lubricating moving parts, checking tire pressure, and adjusting brakes. This helps ensure that all components are in good working order.
-
Proper fitting: Adjust your bike’s saddle height, handlebars, and pedals according to your body proportions for optimal comfort and control while riding.
-
Protective gear: Always wear appropriate protective gear such as helmets, knee pads, elbow guards, and reflective clothing. These can minimize the severity of injuries in case of an accident or fall.
-
Visibility enhancements: Equip your bicycle with reflectors, lights (front and rear), and bells or horns for increased visibility on roads or trails.
Consider the following table depicting statistics related to cycling accidents:
| Type of Injury | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Head Injuries | 45% |
| Fractures | 20% |
| Abrasions | 15% |
| Sprains | 10% |
These numbers serve as a reminder of the potential risks associated with inadequate bike equipment safety measures.
In conclusion, prioritizing bike equipment safety is essential for preventing avoidable accidents during sports cycling. Regular maintenance, proper fitting, wearing protective gear, and enhancing visibility are crucial steps that every cyclist should take to ensure their safety on the road or trail. By being proactive in this regard, cyclists can minimize the likelihood of injuries and enjoy a safer riding experience.
Transitioning into the subsequent section on optimizing performance and injury prevention, let us explore how certain practices can help cyclists improve their overall performance while reducing the risk of cycling-related injuries.
Optimizing Performance and Injury Prevention
Section H2: Ensuring Bike Equipment Safety
Building a strong foundation of bike equipment safety is crucial in preventing cycling injuries. Now, let us explore the next aspect of sports cycling – optimizing performance and injury prevention.
Paragraph 1:
Imagine a scenario where an avid cyclist named Sarah is training for a challenging mountain biking race. To enhance her performance while minimizing the risk of injuries, Sarah focuses on various strategies that go beyond just physical preparation. By understanding how to optimize her performance through efficient techniques and preventive measures, she can ensure a safe and successful experience on the trails.
Paragraph 2:
To optimize performance and prevent injuries in sports cycling, it is essential to consider several key factors:
- Proper nutrition: Fueling your body adequately with balanced meals rich in carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats enhances endurance levels and promotes muscle recovery.
- Appropriate rest periods: Giving your body sufficient time to recover after intense workouts helps prevent overuse injuries and allows for better overall performance.
- Regular cross-training: Engaging in activities such as strength training or yoga helps improve muscular balance, flexibility, and stability, reducing the likelihood of accidents during rides.
- Effective mental preparation: Developing positive visualization techniques and adopting stress management strategies can boost confidence and focus during races or demanding cycling sessions.
These practices not only contribute to improved athletic performance but also foster emotional well-being by:
- Reducing anxiety associated with competitive events
- Increasing self-confidence and motivation
- Enhancing overall enjoyment of the sport
- Promoting a sense of achievement and personal growth
Paragraph 3:
In addition to these guidelines, incorporating proper bike fitment plays a significant role in optimizing both efficiency and comfort during rides. A well-fitted bicycle ensures proper alignment between the rider’s body mechanics and the bike’s geometry. This alignment reduces excessive stress on joints, minimizes discomfort from pressure points, improves pedaling efficiency, and decreases the risk of musculoskeletal injuries.
| Bike Fitment Considerations | Importance |
|---|---|
| Frame size and geometry | Ensures a comfortable riding position |
| Saddle height and angle | Optimizes power transfer and prevents pain |
| Handlebar positioning | Enhances control and reduces strain |
| Cleat alignment | Improves pedaling efficiency |
By integrating these performance optimization strategies into your sports cycling routine, you can elevate both your physical capabilities and mental resilience. Remember, consistent implementation of these practices is key to achieving long-term success in the sport while minimizing the risk of injuries.
Note: It’s important to consult with a professional coach or expert in bike fitting for personalized guidance tailored to your specific needs.